Freenas User wrote: William Grzybowski wrote: We have decided to defer this for now. If anyone can come up with a nicer way to query the hdd temps with a collectd plugin we will happily take it. You just need to type the following command to see cpu temperature in FreeBSD: $ sysctl -a grep temperature OR $ sysctl dev.cpu grep temperature Sample outputs:. Full tutorial: http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/freebsd-determine-processor-cpu-temperature-command/. 802309 ELPRO Cloud is a GxP-compliant self-service temperature monitoring solution. Ideal for practically any size lab, this cloud temperature monitoring system with wireless loT sensors is easy to install, change, and grow. System is GDP, GLP, GMP compliant, CFR 21 Part 11.
How to: monitor Network Attached Storage (NAS) status
In this tutorial it is described how to monitor the complete status of hard disks, SSDs or other storage devices connected over the network with Hard Disk Sentinel - like if they would be directly connected to the computer.
Generally Network Attached Storage (NAS) devices provide no self-monitoring status about them. From the viewpoint of the user (and software) we can read, write files and folders - but it is not possible to identify the hard disks, detect their temperature, health and complete self-monitoring S.M.A.R.T. data, error counters and statistical information. NAS devices sometimes provide internal S.M.A.R.T. checking - but it is not too detailed: it does not provide correct, real time temperature, monitoring about changes / degradations and there may be no alert on different issues.
Hard Disk Sentinel can do all of the above - but only for disk drives connected directly to the computer. Until now.
To access and detect the status information, it is required to 'extend' the functionality of the Network Attached Storage (NAS) devices: to periodically detect and store the current status. These status information reports (status sources in the following) read, interpreted by Hard Disk Sentinel Professional so it displays the appropriate hard disks, SSDs, industrial memory cards and other storage devices like if they'd be connected directly to the actual computer.
Below we discuss about how to extend the functionality of the Network Attached Storage devices (NAS boxes, routers and so) and how to configure Hard Disk Sentinel to read the created status source files.
Hard Disk Sentinel shows complete hard disk status of a NAS drive
Requirements
In order to make things work, we need Hard Disk Sentinel Professional 5.01.8 or newer running on a Windows computer which reads the Status Sources and displays the hard disk status, collect statistics, issue alerts and so. Also we need a Network Attached Storage (NAS) which can produce the Status Source file. The NAS need to have SSH access with root rights for the customization and the user should be familiar about basic Linux commands (knowledge of chmod, cron is at least recommended).
Initial setup of monitoring Network Attached Storage (NAS) devices
The most important is that the Network Attached Storage device should provide SSH access in order to extend its functionality. Some devices may support it out-of-the-box or support it via official plug-in (like the D-LINK DNS327L . Some others may require tweaks, add-ons (like the fun-plug used with D-LINK DNS320LW if used with older firmware) or even special firmware. Please note that unofficial modifications, firmware updates may void warranty so please be careful! Personally I do not recommend such actions, if you're not sure, ask the manufacturer about the situation as they can assist about SSH access (or hopefully for increased number of requests, they may add the required functions in a future official release to make things easier).
Please note that due to high number of different devices, firmware, it would be impossible to provide step-by-step guide for all devices, but I try to show the idea generally and illustrate with some devices, hopefully this helps in making changes on the actual device.
You'll need to have SSH client, for example PUTTY. You can download directly from this link: putty.exe
Create status source by using Hard Disk Sentinel Linux version
Start PUTTY and log in to the NAS device as root.
Locate a folder which is readable over the network (shared with samba) from the remote computer running Windows and Hard Disk Sentinel Professional by entering cat /etc/samba/smb.conf
Shared folders
The folder /shared/ shared on the network, so we should create status source in that folder. Advanced users may even create a new, different share just for this purpose by editing the samba configuration file.
Create a folder for Hard Disk Sentinel executable, by entering mkdir /hdsentinel Photoshop libreoffice download.
Then open this folder by entering cd /hdsentinel
Download Hard Disk Sentinel Linux version designed for ARMv5 CPU by entering wget http://www.hdsentinel.com/hdslin/armv5/hdsentinelarm
Use chmod to enable executable permissions: chmod 755 hdsentinelarm (Hard Disk Sentinel Linux Edition page describes this with details)
Enter crontab -e to edit cron jobs and create a scheduled task: to start Hard Disk Sentinel Linux edition which should save a report (the Status Source) in a folder, which is readable over the network (see cron reference about detailed information and options). Add the following line at the end of the list of possible configured cron jobs:
*/10 * * * * /hdsentinel/hdsentinelarm -r /shared/hdsreport.html -html
Then press CTRL+X to exit and save the updated list. By this new entry in crontab, the Linux HDsentinel (which downloaded in the /hdsentinel folder) launched every 10 minutes and it saves report to /shared/hdsreport.html file which is accessible over the network.

After some time (10 minutes or fewer, depending the actual clock) hdsreport.html file created and saved. This hdsreport.html file contains the complete status of all found hard disk drives, SSDs, flash drives, industrial memory cards and so. The file can be opened in any web browser to quickly check the status of the devices, even outside (without installation of) Hard Disk Sentinel Professional, which is an instant advantage and by this, the NAS functionality is improved. If the NAS device supports external USB port(s) for additional storage, external hard disk(s) connected there also automatically enumerated, detected and reported.
Load status source in Hard Disk Sentinel Pro
When the status source(s) configured to be created and automatically updated by the NAS, it is required to configure Hard Disk Sentinel Professional running on the Windows computer to use it: read, process and display the contents. For this, please select File menu ->Configure NAS Disk Monitoring.
Configure NAS Disk Monitoring in Hard Disk Sentinel Professional
In this window, it is possible to add any number of status sources by
performing automatic detection which scans the root folder of all network mapped drives and automatically add found hdsreport.html files. So if the shared folder of NAS drive is mapped as network shared drive, then it is only required to click the Auto Detect button.
browse the file system and select the appropriate network location or specify the network path. UNC path names are supported, for example nas-devicehdsreport.html
specify complete path and file name directly or specify http:// connection, so even web servers or distant servers can be monitored this way
Hard Disk Sentinel Professional automatically attempts to connect and read the file and shows the amount of hard disk(s) found in the configured Status Source.
After clicking OK in this window, the Status Source(s) processed and the hard disk drive(s) displayed just like disk drives connected directly to the actual computer (internally or by USB / eSATA).
Freenas Temperature Monitoring
Hard Disk Sentinel Professional shows Network Attached Storage disk drives with different (light orange) background to indicate that these devices are not direct connected disk drives - but attached to the network.
The connection state symbol in the upper right corner shows the actual status: green if all configured Status Sources could be read and processed - red if one (or more) Status Sources unreadable (network error).
Then, in all following perioidc detection cycles, Hard Disk Sentinel will attempt to read and update the disk status, issue alerts if required. If you prefer to cancel or adjust monitoring, it is possible in the File menu ->Configure NAS Disk Monitoring window, where it is possible to edit the Status Source location (for example if the device changed name, IP address or so) or delete the Status Source from the list.
If you prefer to disable creation of Status Source files on the NAS itself, you can log in by SSH and remove the entry from cron jobs, delete the saved software and its associated folder too.
Note: Un-registered (trial) Hard Disk Sentinel Professional version allows configuring Status Source(s) for evaluation purposes but on restart, the setting automatically discarded (need to be configured again). Also the trial version shows partial information on the S.M.A.R.T. page only. The registered (complete) version keeps the configured setting and displays the complete status automatically after restarts. Hard Disk Sentinel standard version does not support NAS monitoring, only Hard Disk Sentinel Professional has this option.

Start PUTTY and log in to the NAS device as root.
Locate a folder which is readable over the network (shared with samba) from the remote computer running Windows and Hard Disk Sentinel Professional by entering cat /etc/samba/smb.conf
Shared folders
The folder /shared/ shared on the network, so we should create status source in that folder. Advanced users may even create a new, different share just for this purpose by editing the samba configuration file.
Create a folder for Hard Disk Sentinel executable, by entering mkdir /hdsentinel Photoshop libreoffice download.
Then open this folder by entering cd /hdsentinel
Download Hard Disk Sentinel Linux version designed for ARMv5 CPU by entering wget http://www.hdsentinel.com/hdslin/armv5/hdsentinelarm
Use chmod to enable executable permissions: chmod 755 hdsentinelarm (Hard Disk Sentinel Linux Edition page describes this with details)
Enter crontab -e to edit cron jobs and create a scheduled task: to start Hard Disk Sentinel Linux edition which should save a report (the Status Source) in a folder, which is readable over the network (see cron reference about detailed information and options). Add the following line at the end of the list of possible configured cron jobs:
*/10 * * * * /hdsentinel/hdsentinelarm -r /shared/hdsreport.html -html
Then press CTRL+X to exit and save the updated list. By this new entry in crontab, the Linux HDsentinel (which downloaded in the /hdsentinel folder) launched every 10 minutes and it saves report to /shared/hdsreport.html file which is accessible over the network.
After some time (10 minutes or fewer, depending the actual clock) hdsreport.html file created and saved. This hdsreport.html file contains the complete status of all found hard disk drives, SSDs, flash drives, industrial memory cards and so. The file can be opened in any web browser to quickly check the status of the devices, even outside (without installation of) Hard Disk Sentinel Professional, which is an instant advantage and by this, the NAS functionality is improved. If the NAS device supports external USB port(s) for additional storage, external hard disk(s) connected there also automatically enumerated, detected and reported.
Load status source in Hard Disk Sentinel Pro
When the status source(s) configured to be created and automatically updated by the NAS, it is required to configure Hard Disk Sentinel Professional running on the Windows computer to use it: read, process and display the contents. For this, please select File menu ->Configure NAS Disk Monitoring.
Configure NAS Disk Monitoring in Hard Disk Sentinel Professional
In this window, it is possible to add any number of status sources by
performing automatic detection which scans the root folder of all network mapped drives and automatically add found hdsreport.html files. So if the shared folder of NAS drive is mapped as network shared drive, then it is only required to click the Auto Detect button.
browse the file system and select the appropriate network location or specify the network path. UNC path names are supported, for example nas-devicehdsreport.html
specify complete path and file name directly or specify http:// connection, so even web servers or distant servers can be monitored this way
Hard Disk Sentinel Professional automatically attempts to connect and read the file and shows the amount of hard disk(s) found in the configured Status Source.
After clicking OK in this window, the Status Source(s) processed and the hard disk drive(s) displayed just like disk drives connected directly to the actual computer (internally or by USB / eSATA).
Freenas Temperature Monitoring
Hard Disk Sentinel Professional shows Network Attached Storage disk drives with different (light orange) background to indicate that these devices are not direct connected disk drives - but attached to the network.
The connection state symbol in the upper right corner shows the actual status: green if all configured Status Sources could be read and processed - red if one (or more) Status Sources unreadable (network error).
Then, in all following perioidc detection cycles, Hard Disk Sentinel will attempt to read and update the disk status, issue alerts if required. If you prefer to cancel or adjust monitoring, it is possible in the File menu ->Configure NAS Disk Monitoring window, where it is possible to edit the Status Source location (for example if the device changed name, IP address or so) or delete the Status Source from the list.
If you prefer to disable creation of Status Source files on the NAS itself, you can log in by SSH and remove the entry from cron jobs, delete the saved software and its associated folder too.
Note: Un-registered (trial) Hard Disk Sentinel Professional version allows configuring Status Source(s) for evaluation purposes but on restart, the setting automatically discarded (need to be configured again). Also the trial version shows partial information on the S.M.A.R.T. page only. The registered (complete) version keeps the configured setting and displays the complete status automatically after restarts. Hard Disk Sentinel standard version does not support NAS monitoring, only Hard Disk Sentinel Professional has this option.
Alternative Status Sources
To monitor network attached storage where Hard Disk Sentinel is not available (for example on FreeBSD / FreeNAS systems) it is possible to use smartctl tool to export disk status information and use it as status source for Hard Disk Sentinel Professional.
For this, after logging in to the device with SSH, please configure this command as scheduled task:
/usr/sbin/smartctl -r ataioctl,2 -d sat -a /dev/sda > /shared/smartsda.txt
This creates smartsda.txt file in the /shared folder (assuming that it is shared - but you may use cat /etc/samba/smb.conf to find out the folder which is available over the network about /dev/sda device. The important is to keep the -r ataioctl,2 section as this enables logging of 'raw' disk information (identification and self-monitoring data) which is not processed/translated/interpreted in any ways. You may need to modify the device name (/dev/sda), the device detection method (-d sat) too. Plus you'll need to create different schedule for each of the device(s) you prefer to monitor and add all such status sources one-by-one into Hard Disk Sentinel Professional.
Depending on the actual system, smartctl may be located in different folder, for example /usr/local/modules/bin/smartctl or something else. Using find / -name 'smartctl' command may help to find the tool.
The benefit of this method is that it is not required to download any software, just use the available smartctl for detection. However it may be not as flexible or useful - so where possible, is is better to use Hard Disk Sentinel instead because there are many benefits:
Easier configuration: no need to manually check/specify device nodes, detection/device type
Follows device configuration changes automatically (removable drive inserted/removed if the NAS supports USB slot)
Single report created for multiple disk drives / devices
Created HTML report can be opened any time by any browser to check actual, complete status independently from Hard Disk Sentinel Pro running on Windows
Supports devices (RAID boxes, industrial SD memory cards)
Safer report creation and update in a single step
Example step-by-step tutorial
Monitor hard disk status of D-Link DNS327L NAS (tutorial with images)
Monitor hard disk status of Synology DS416play NAS with DSM 6 (PDF) Tutorial by Marcus Wagner
Monitor hard disk status of Buffalo Linkstation Live NAS LS-CHL (PDF) Tutorial by Henry Pollock
Monitor hard disk status of Seagate D4 NAS (PDF) Tutorial by Gary Ryan
Monitor hard disk status by docker / Synology docker Tutorial by Alex Balcanquall(HDSentinel Docker Repo) Tested on Synology DS1815+ and DS918+
Monitor hard disk status of THECUS NAS (PDF) Tutorial by Patric Eberle
Monitor hard disk status of NETGEAR READYNAS (PDF) Tutorial by John
Monitor hard disk status of ASUSTOR AS6202T NAS (PDF) Tutorial by Mario Winklmeier
Monitor hard disk status of WD MyCloud 1st Gen (FW 04.xx.xx) (PDF) Tutorial by Krzemien
Freenas Temperature Monitor Manual
Call to arms: NAS users who can create and share (to help other users) a short step-by-step tutorial to illustrate functionality with their device(s), we can offer lifetime license (with lifetime free updates) of Hard Disk Sentinel Professional Family license. Please contact at info (at) hdsentinel (dot) com for details.
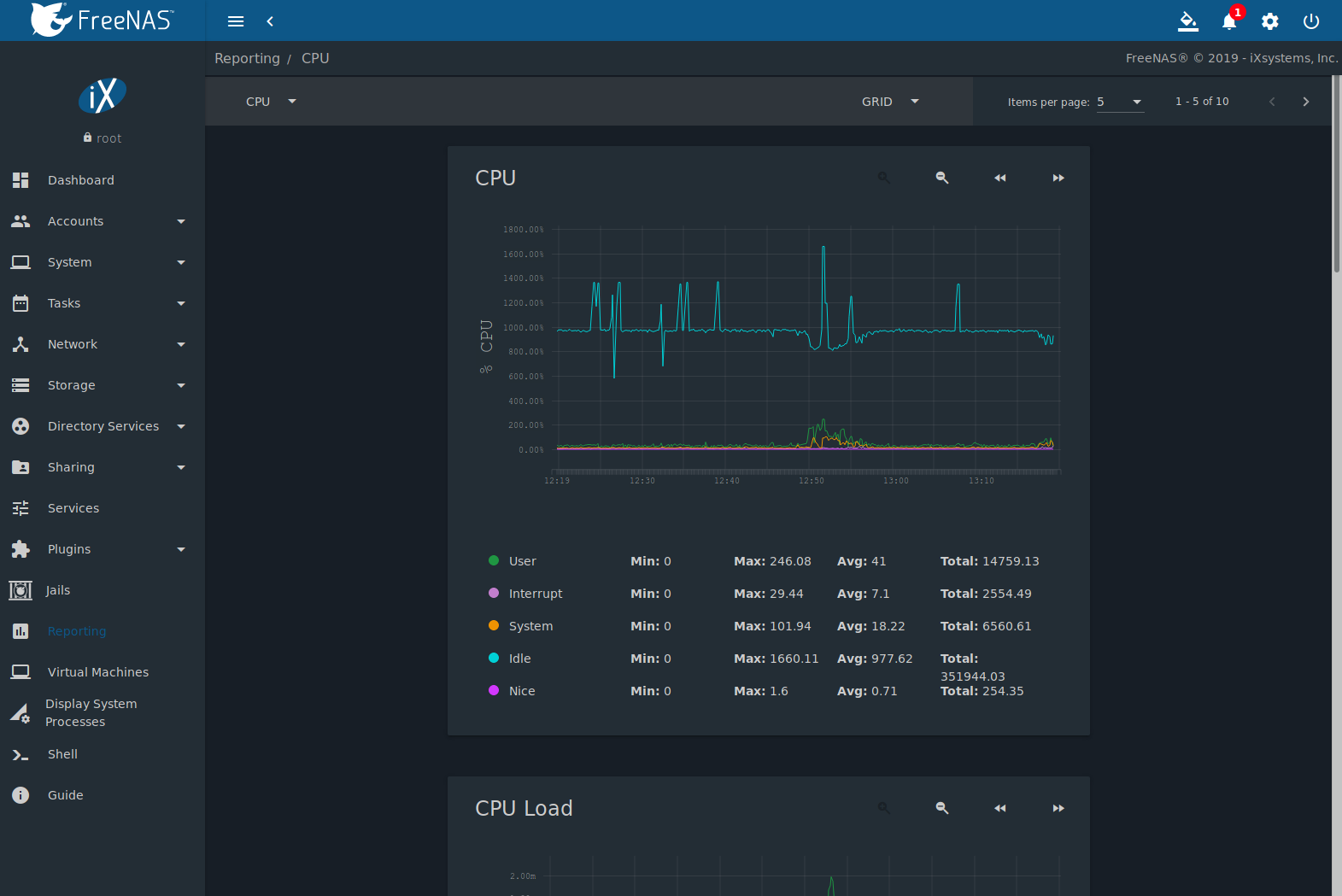
Reporting displays several graphs, as seen inFigure 16.1. Choose a category from thedrop-down menu to view those graphs. There are also options to changethe graph view and number of graphs on each page.
FreeNAS® usescollectdto provide reporting statistics. For a clearer picture, hover over apoint in the graph to show exact numbers for that point in time. Use themagnifier buttons next to each graph to increase or decrease thedisplayed time increment from 10 minutes, hourly, daily, weekly, ormonthly. The << and >> buttons scroll throughthe output.
Note
Reporting graphs do not appear if there is no related data.
Graphs are grouped by category on the Reporting page:
CPU
- CPUshows the amount of time spent by the CPU in various statessuch as executing user code, executing system code, and beingidle. Graphs of short-, mid-, and long-term load are shown, alongwith CPU temperature graphs.
Sid meier's civilization 6 cheats. Disk
- Diskshows read and write statistics on I/O, percent busy, latency,operations per second, pending I/O requests, and disk temperature.Choose the DEVICES and METRICS to view theselected metrics for the chosen devices.
Note
Temperature monitoring for the disk is disabled ifHDD Standby is enabled in Disks.
Memory
- Memorydisplays memory usage.
- Swapdisplays the amount of free and used swap space.
Network
- Interfaceshows received and transmitted traffic in megabytes per second foreach configured interface.
NFS
- NFS showsinformation about the number of procedure calls for each procedureand whether the system is a server or client.
Partition
- Disk spacedisplays free, used, and reserved space for each pool and dataset.However, the disk space used by an individual zvol is notdisplayed as it is a block device.
System
- Processesdisplays the number of processes. It is grouped by state.
Target
- Target shows bandwidth statistics for iSCSI ports.
UPS
- UPSdisplays statistics about an uninterruptible power supply(UPS) usingNetwork UPS tools.Statistics include voltages, currents, power, frequencies,load, and temperatures.
ZFS
- ZFSshows compressed physical ARC size, hit ratio, demand data, demandmetadata, and prefetch data.
Reporting data is saved to permit viewing and monitoring usage trendsover time. This data is preserved across system upgrades and restarts.
Data files are saved in /var/db/collectd/rrd/.
Warning
Freenas Hdd Temperature Monitor
Reporting data is frequently written and should not bestored on the boot pool or operating system device.

